When done well, data-driven marketing is the best way of making marketing processes efficient, performance-oriented and successful. Our ultimate guide explains in four clear steps how you can approach the challenges of building a data-driven strategy in the right way and which tools you need to reach your objectives.
Looking to see what advantages a data-driven approach could bring to your marketing activities? Then why not see how our Digital Strategies Group can help you?
This guide covers the following topics:
- What is data-driven marketing?
- Why did data-driven marketing evolve?
- Why is data-driven marketing important?
- How does data-driven marketing work?
- Which tools are needed for data-driven marketing?
Definition: What is data-driven marketing?
Data-driven marketing is an approach to online marketing that uses data to increase the level of targeting, personalization and ultimately the success of campaigns and communications. Data helps create marketing activities that are precisely tailored to the needs of the user: Less scatter-gun, more sniper rifle.
A data-driven marketing strategy is one that is based on a solid data analysis. Insights arm digital marketers with genuine understanding of the behavior and interests of their users. This enables businesses to reach potential customers with relevant messaging, at the right time and at each specific point of the customer journey, creating as personal as possible an experience for each user.
With data, marketing is transformed from a traditional mass-market approach to a personalized approach.
Hypothesis: Marketing decisions that are made based on a solid data analysis are good decisions. Data insights increase reach, branding and user engagement in a measurable way.
- Customers are addressed in a more individual way which improves the customer experience.
- Performance is measured more precisely and efficiency/ROI are increased.
- Performance is improved.
Background: Why did data-driven marketing evolve?
Data-driven marketing evolved because three central aspects of marketing changed: The user, the user journey and the data basis.
The central character in any marketing story is the user – the person who marketing activities are trying to reach. Today’s user is better informed, better connected and more demanding than ever before. They expect personalized messages that are created just for them and that appear relevant to their specific needs. To make this possible, marketers obviously have to know exactly who their users are.
Know your users!
If they hope to reach their users, marketers can no longer rely on traditional, linear customer journey structures. Today, people jump between numerous touchpoints on all kinds of devices and channels. At each touchpoint, it is the marketer’s task to reach out with an attractive message. This can only be successful if marketers know where their users are and what they are looking for there.
Know their journey!
At each touchpoint, the user leaves an information trail that can be used to gain valuable insights. The data can be used to create user profiles that analyze and understand consumer behavior. This shows us:
- who they are, what their world looks like, what their needs are and what they are looking for.
- which point of the user journey they’re currently, how and when they’re accessing which kinds of information.
Use the data!
This lets marketers target users with messaging and products that are relevant for each touchpoint.
“Data-driven content marketing lets us engage in a dialogue with our customers. We are interacting with them. We want them to value our companionship and perceive us as someone they can talk to whenever they like to gain offer new insights, inspiration and relevant information.” – Michael Dziewior, Team Lead Content Services, Searchmetrics Digital Strategies Group
Why is data-driven marketing important?
So you can address customers efficiently and individually, meaning that you are right on point. Data is knowledge is power is success. Today, data are the foundation of long-term value creation. They make it possible to gain insights that enable the precise adaption of marketing activities to the needs of the consumer.
The advantages at a glance
Data-driven marketing helps to…
- reach customers more effectively
- Understand interactions with customers at all touchpoints of the customer journey
- Personalize communication at all touchpoints of the customer journey
- Adapt communication to current and important trends
- Increase customer service, satisfaction and loyalty
- Strengthen brands and improve branding
- increase efficiency
- Precisely measure the success of campaigns
- Measurably increase the Return on Investment (ROI) of campaigns
- Save resources by investing media budget in a more focused way, targeting high-potential audiences with a higher likelihood of conversion
- improve performance
- Significantly increase the success of campaigns
- Encourage purchase decisions by creating personalized offers
According to 57% of those surveyed for a Forbes Study, the ROI of their data-driven marketing campaigns had seen a measurable increase.
How does data-driven marketing work?
The aim of data-driven marketing is finding out what works and then doing more of it. To achieve this, data is pooled from numerous sources and transformed into actionable insights. These form the basis for a marketing strategy that includes all important channels: paid media, corporate media and earned media.
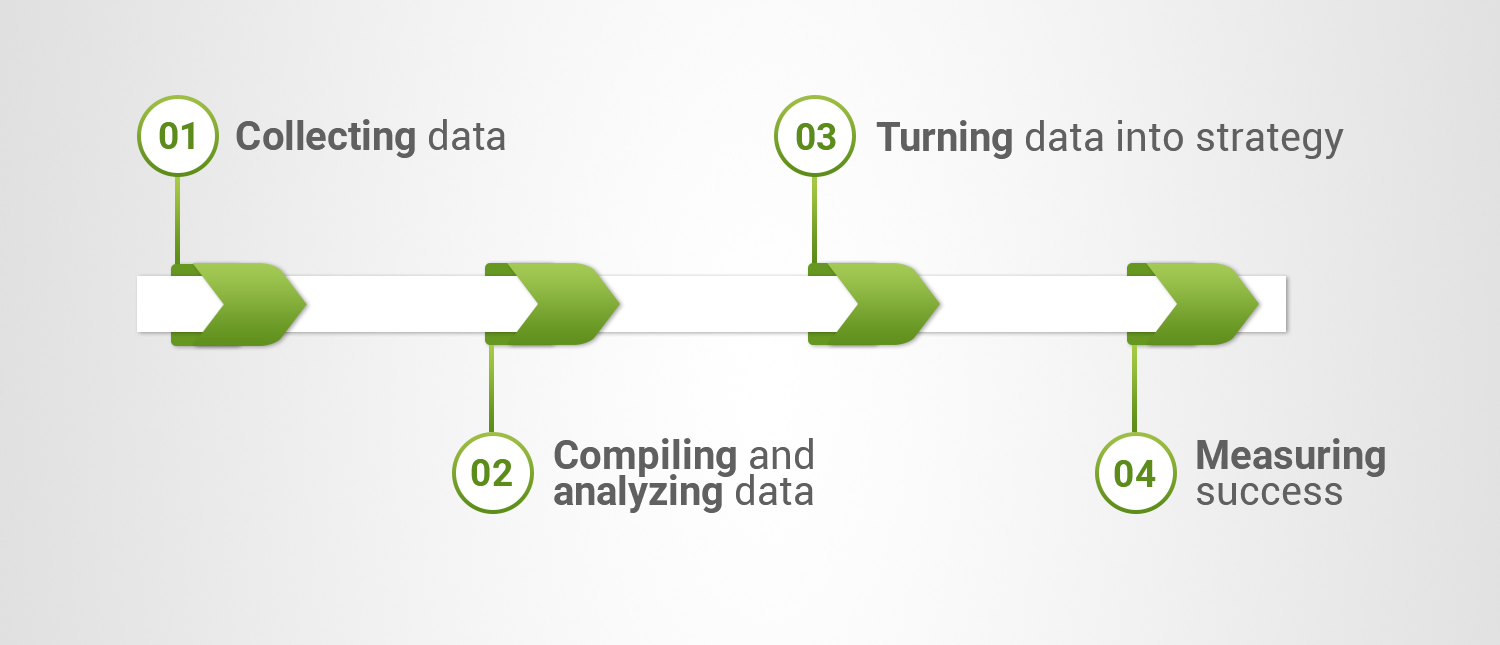
The process can be viewed in four steps:
- Collecting data
- Compiling and analyzing data
- Turning data into strategy
- Measuring success.
1. Collecting data
There are countless possible sources that data can be taken from and the volume of data is enormous. New contact points between companies and customers emerge constantly; new information is generated at each stage of the customer journey: online and offline, mobile and social, locally and through market research.
To collect customer data effectively, there are two questions that need answering:
- Which data is needed in order to understand the user and their decision-making process?
- Which data sources are available and relevant?
Traditional marketing sorts users into rough target groups. The data-driven approach is more precise: Personas are used to create micro-targets, that – thanks to detailed data – are extremely clearly defined. In this way, online marketers generate different content for a tech-savvy student than they do for a music-loving student.
| Target group | Persona |
| Demographic and socio-economic categories:
Age, gender, marital status, place of residence, family size, education, occupation, income. |
Additional psychographic factors, such as:
Life style, values and opinions, interests, hobbies and purchase behavior. |
Data sources
Data for generating personas can come from online and offline sources. These are:
- First-party
- The company’s own data, such as CRM data or user data from tracking on the company website – web-browsing behavior, website navigation or online interactions and purchase behavior in the company’s online shop.
- Second-party
- Company data, but gained using non-proprietary services, such as data from marketing partners or online search behavior data measured using Google Analytics or the Google Search Console.
- Third-party
- Data from professional data providers, collected using various methods and purchased by the company. Could include data on search volume, trends, seasonality, user intent etc.
2. Compiling and analyzing data
The biggest challenge of data-driven marketing is turning Big Data into Smart Data – this means filtering out the relevant information from the vast amounts of data collected from online and offline sources, and converting this information into insights that can be used to drive actions.
Big Data Analytics is the magic word. It is used in the field of Business Intelligence to optimize internal company processes. Data is extracted from various sources, centralized and compiled in a uniform format so that it can then be meaningfully categorized.
For marketing that aims to be driven by data, the technical complexity has to be minimized as much as possible. Efficient analysis requires the right tools that interact seamlessly with each other. Also, organizational structures also need to be in place that work in a connected, integrated way, rather than operating in silos.
3. Turning data into strategy
The insights gained from the data analysis are used to create an integrated marketing strategy. This should include a clear definition of the goals and KPIs, and establish where the greatest opportunities are. It should be clear whether the (primary) aim is brand awareness, lead generation, sales or web traffic. It should be clear from the data where most traffic comes from, which channels and pages convert the best and at which stage of the customer journey most users exit the sales funnel.
The marketing strategy should be composed in a holistic way to incorporate and integrate different digital and analogue channels. These could include email marketing and SEO, partnerships and events, as well as SEA, display advertising, retargeting, influencer marketing and offline advertising. Data-driven content can also be part of this mix: Which questions does the user have, which features do they want, which content are they looking for?
Examples of application:
- Identify personas
- Use seasonality and trends to create editorial and paid media calendars
- Use seasonality and trends to create relevant website content
- Run personalized email campaigns targeting customers’ specific preferences
- Promote the right products on the right marketing channels by predicting which product a customer will be interested in
- Set up automatically triggered emails following specific actions that a user makes on the company website
- Increase efficiency of advertising purchases
Read about Casper’s data-driven content strategy
3. Measuring success
As one of a company’s key objectives is increasing efficiency, measuring performance is clearly of central importance. The factors to be measured depend on the company‘s objectives.
The following is a summary of the most important performance KPIs for online marketing:
- Objective: Customer loyalty and traffic quality
- Bounce rate
- Average session length
- Average page views per session
- Retention rate: Active customers today / active customers a defined length of time ago
- Objective: Customer satisfaction
- Bounce rate
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- Objective: Profitability
- Cost per buy (ROI): Profit / Total cost of an investment
- Conversion rate for each channel and each page, based on target conversions, such as
- Newsletter sign-ups
- Whitepaper downloads
- Trial version registrations
- Objective: Gain new customers
- Cost per acquisition
- Acquisition rate
- Objective: Strengthen brand
- Impressions
- Rankings
- Mentions on social media channels
- Objective: Website visits
- Traffic
- Sessions
Which tools are needed for data-driven marketing?
The right tools for the right task
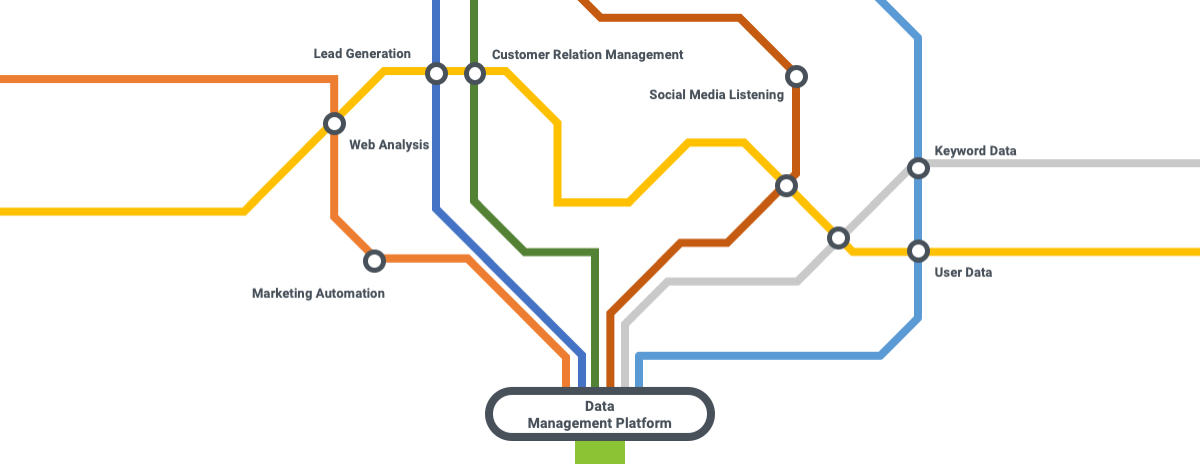
Data-driven marketing can only be successful if it is approached holistically. To achieve this, the market offers a huge number of tools that can be used for different purposes, such as collecting, compiling, analyzing, preparing, visualizing and utilizing data. The tools can be sorted into seven main areas of application:
- Web analysis: e.g. Google Analytics, Google Search Console, Searchmetrics Suite
- Social media listening: e.g. Buzzsumo, Brandwatch, Sysomos, Meltwater, Vico, Buffer, Oktopost
- Marketing automation platforms: e.g. Oracle Eloqua, Marketo, Hubspot, Silverpop
- Customer relationship management (CRM): e.g. Salesforce, Sugar
- Reporting and analysis: e.g. DataHero, DataStudio, Tableau, Domo, Qlik
- Lead generation: e.g. LeadFuze, LinkedIn Lead Gen Forms, Rapportive
- Content strategy and creation: e.g. Searchmetrics Research Cloud and Content Experience, Atomic Reach, Grammarly, Hemingway Editor, Curata, Canva
DMP: Untangling the web and joining the data dots
With the huge number of tools available, the demand for a central platform is growing. Companies hope to move away from silos and enable cross-departmental cooperation – with marketing, IT, business analytics and product development working together. The idea is that different data should no longer be restricted to different areas, but that all data should be accessible for all systems.
The solution to this challenge is provided by Data Management Platforms, or DMPs, also known as Marketing Data Warehouses. These technologies act as a “data headquarters”, and help companies to extract information from different sources so that it can then be consolidated, organized and analyzed. A DMP contains a database and an array of features used for data processing. The main features of a DMP are:
- Collecting, saving and classifying data from different data sources
- Data analysis, creating reports and data visualization
- Data segmentation e.g. along target group lines
- Data activation
- Data optimization to continually fine-tune targeting criteria
Relevant tools include The Adex, Adobe Audience Manager, Lotame, Mediamath and OneID from Neustar.
Wrap-up
A data-driven marketer can reach their high-potential customers with the right marketing messages at the right time in the right place. Instead of implementing individual measures, holistic eco-systems are created with the customer at its center. This makes campaigns more efficient, more successful and more measurable.
If you’d like to see for yourself which benefits a data-driven approach can bring to your marketing activities, then you can arrange an appointment with our Digital Strategies Group and see how our consultants can help you.